Edge Computing: Use Cases and Benefits in the Automotive and Motor Insurance Industry | Inspektlabs
Edge computing helps improve the efficiency of various applications, including autonomous driving, auto insurance claim processing, and vehicle inspections.

This post will cover Edge computing, its relevance, and applications in the automotive and motor insurance industries. We begin with an introduction to the basics of Edge computing to establish a foundation for our discussion.
Then we will discuss the related advantages and challenges. Our discourse will cover Edge computing's applications in the automotive and motor insurance industries.
Lastly, we will cover how Inspektlabs leverages Edge computing to facilitate a seamless inspection framework for auto industry players before concluding.
Table of Contents
The Challenges of Edge Computing
How Can Businesses Overcome These Challenges?
Applications Of Edge Computing In The Automotive Industry
The Applications Of Edge Computing In The Motor Insurance Industry
What Is The Relevance Of Edge Computing In Automating Vehicle Inspections?
Introduction
Advancements are being facilitated at unprecedented rates due to the ever-expanding capabilities of new-age technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, cloud computing, and many others.
One such technology, Edge computing, has yet to garner mainstream recognition outside the scientific community. However, over the coming years, we can expect a monumental shift in this regard.
According to a recent McKinsey report, less than 20% of the data produced by businesses is ultimately used due to latency issues and the expense of transporting data across environments. [Source: McKinsey]
Edge computing facilitates better latency and reduces costs. Therefore, the global expenditure on Edge computing may reach $250 billion by 2025, with a ~10% CAGR. [Source: McKinsey] Now that we have briefly contextualized this technology's potential impact let us explore it in-depth to strengthen our fundamentals.
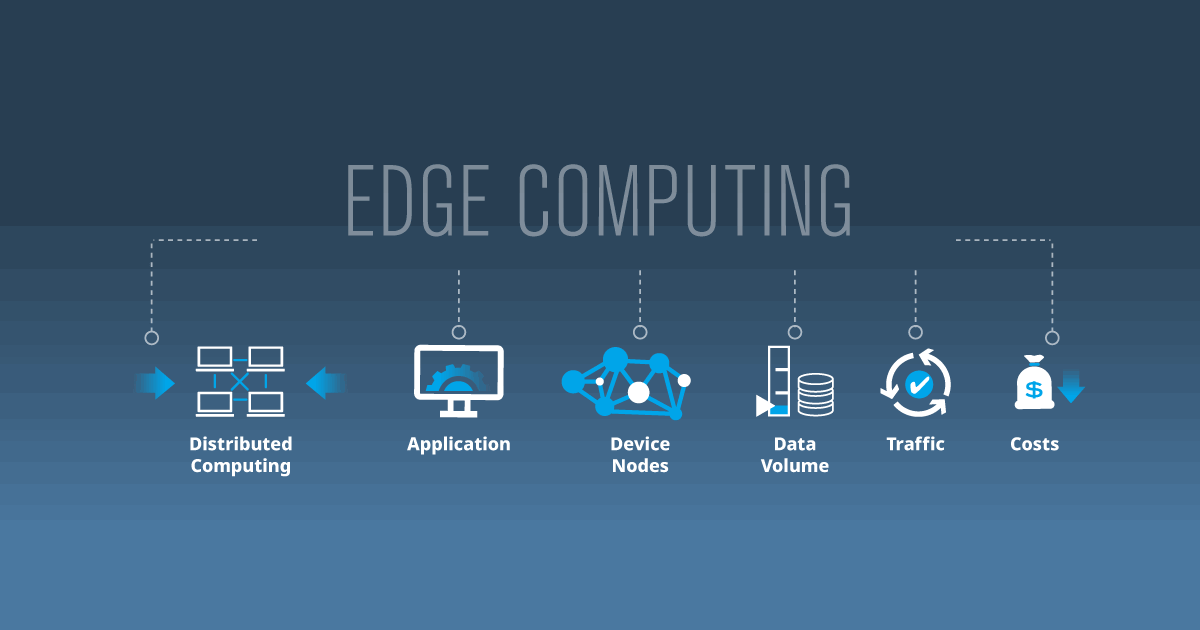
What is Edge Computing?

It is a class of distributed computing where resources are deployed at the so-called "network Edge." The technology works by allowing a device to generate and process data at the location where it's generated. Doing this can reduce the need for bandwidth, which can be expensive.
Furthermore, the processing can happen in real-time, allowing more timely decision-making. This can be done with various devices, such as mobile point-of-sale kiosks, industrial PCs, or smart cameras. By leveraging these technologies, companies can gain faster, more accurate, and more reliable data processing. [Source: Research Gate]
An example of an Edge-based application is Apple's Face ID feature. Users can train their iPhones to recognize their faces. When a facial recognition test is run, it takes a few milliseconds to perform.
Apple manages this process through the devices—similarly, streaming video platforms cache information for lower latency. In the following segment, we will look at the applications and advantages of Edge computing in a broader context.
Advantages of Edge Computing
As the magnitude of connected devices increases, transferring data from one place to another becomes harder. However, Edge computing solutions can keep the most critical data at the Edge while waiting for the rest to become available.
With Edge computing, data can be processed on the spot and is more secure because it is kept close to end users. Additionally, some of the application's functions can be stored locally to minimize costs.
This is an excellent solution for companies with limited bandwidth, which is arguably true for every company. The technology can also help companies make the most of their data at every point in the process.
Aside from that, it can also provide improved customer experiences and increased efficiencies. Some benefits include faster response times, decreased bandwidth usage, and increased security. Let us cover a few benefits:
Enables Better User Experiences – One of the reasons why Edge networks are so popular is because it allows for a much better user experience. It keeps the most relevant data at the network's Edge, reducing latency and bandwidth costs.

Mitigates Security Risks – Edge computing also reduces security risks. By storing data on Edge devices, organizations are protected from cyberattacks.
Edge devices are less likely to be targeted than traditional, centralized data centers. Furthermore, it is more difficult to breach the organization's network's Edge.
Optimizes IoT Applications – As an industry, the Internet of Things is growing at an incredible pace. Over 30.9 billion IoT units are expected to be in use by 2025, compared to 13.8 billion units in 2021. [Source: Statista]
This is a great way to optimize IoT applications. Not only does it avoid bandwidth issues, but it also decreases the time needed to process data. For example, operating an autonomous vehicle on Edge is much easier than in the cloud.
The Challenges of Edge Computing
While Edge computing offers numerous benefits, as we have outlined before, some challenges and limitations exist:
Scalability – One of the biggest challenges in Edge networks is the ability to scale over the long term. Businesses will need to be able to support hundreds to thousands of Edge devices. If they cannot do this, the Edge computing strategy fails.

Hardware Limitations of Edge Devices – Another major challenge is the hardware. Edge networks are not designed to handle as much hardware as a full-scale data center. Furthermore, Edge devices are also subject to hardware failures. However, if businesses can reduce the hardware hurdles, they will be better positioned to take advantage of Edge networks.
Limited Computation Capabilities – Edge devices, like smartphones, cannot host large ML models owing to their limited computation capabilities.
Connectivity Constraints – Another big challenge is limited connectivity in remote areas. Edge devices rely on being connected to a central cloud, which can be pretty challenging to facilitate in remote areas. Also, network latency can interfere with the performance of the applications.
How Can Businesses Overcome These Challenges?
The Edge computing landscape is still in its early stages and has its fair share of challenges. This means businesses have to conduct due diligence when forming Edge infrastructures.
It also means they must ensure that the security measures are up to date. Edge applications should be sophisticated, with features like raw data stream processing, fault tolerance, and message brokering for event-based applications.
They should also be low on computing footprint and technical IT overhead. Let us cover the potential solutions:
- Connectivity – Connectivity is a problem that can handicap the entire Edge framework. Thus, businesses must establish mechanisms for managing Edge devices without data connectivity. For backup or supplementary control and connectivity, businesses can ensure that their Edge networks have the facilities for a second connection.

- Security - Every unit is a network asset that may be compromised, creating numerous vulnerable points in the Edge network. Therefore, businesses must ensure that the security coverage extends to IoT and sensor devices. Technologies that prioritize preventing and detecting intrusions and vulnerability management should be used.
- Network Administration – Remote administration and management are crucial for Edge installations due to their remote and possibly inhospitable environments. IT administrators must be able to monitor functions at the network Edge and undertake suitable measures to address the concerns.
- Physical Maintenance – It is essential to remember the need for the physical maintenance of Edge devices. With the demand for regular equipment and battery changes, connected devices have limited lifespans.
Edge equipment may suffer malfunctions and demand maintenance or replacement. Regular maintenance is thus indispensable for site logistics.
Applications Of Edge Computing In The Automotive Industry
Edge computing can be utilized in many industries, including automotive, motor insurance, healthcare, public safety, manufacturing, retail, and transportation. [Source: McKinsey]
Manufacturers are using Edge devices to improve production. Also, banks use Edge devices to store sensitive financial information in the financial industry. However, in this post, we will focus on the applications of Edge networks in the motor insurance and automotive industries.
Edge computing offers many benefits compared to the traditional automotive computing model, which relies on an onboard processor and a centralized data processing warehouse.
For example, it allows automakers to manage better their vehicles' data, such as fuel consumption and temperature. Also, it reduces the amount of data being sent out of the car, thus decreasing the need for a centralized data-processing hub.
There is a large and promising market for innovative solutions. Although the automotive industry is a legacy industry, digital native start-ups like Inspektlabs are pushing the industry forward.
Some of the most exciting applications will likely include vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) protocols, which require Edge-based IoT devices to be installed across the automotive ecosystem.
Another exciting application is the use of AI to improve the performance of connected cars. Let us look at these examples in more detail.

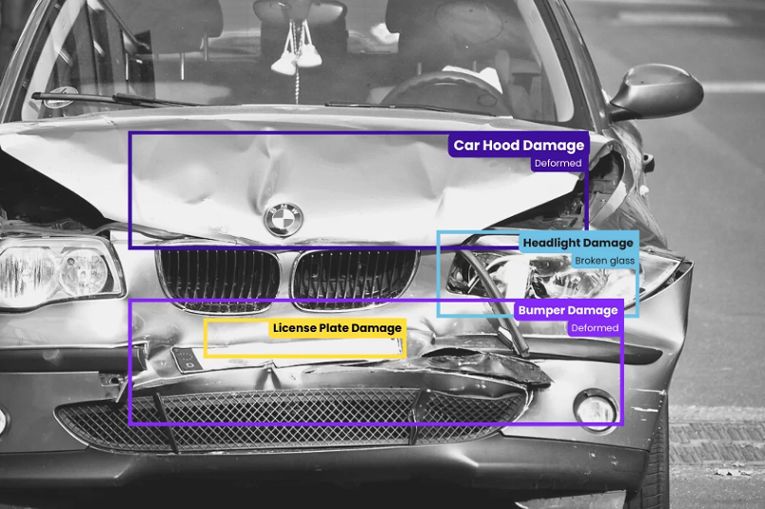
- Automated Vehicle Inspections – Many steps are involved in the inspection process, each requiring a specialized model. One solution to this problem is automated vehicle inspections. However, processing latency can negate automation efficiencies when done in the cloud.
Fortunately, Edge computing can improve speed and reduce latency. With edge computing, inspection data is processed closer to the vehicles. This can allow decisions to be made in milliseconds. In addition, it can improve workflows and reduce downtime.
- Condition-Based Vehicle Repairs – Edge computing frameworks facilitate real-time tracking and reporting vehicle conditions through telematics. Using Edge computing solutions makes it possible to analyze data and make decisions based on real-time information.
Having this kind of data can allow for predictive maintenance schedules. Moreover, it will help to prevent accidents and ensure a safer driving experience.
- Connected Cars - Edge networks are an essential component of connected cars. These are vehicles equipped with sensors and actuators that can help gather and analyze large amounts of data in real time.
When combined with advanced driver assistance systems and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) technologies, Edge computing helps improve the performance of connected vehicles.

- Cost Reduction - Edge networks are among the critical enabling technologies in the automotive industry. This decentralized form of computing provides computing power near the data source to reduce latency and data transmission costs.
- Efficient Ecosystems - One of the most critical aspects of using Edge Computing in the automotive space is the ability to create a streamlined and integrated ecosystem. With many technologies to consider, auto manufacturers need to develop a well-rounded and dependable solution.
Moreover, they must take advantage of new AI and machine learning innovations. By integrating Edge computing with existing and emerging cloud and big data platforms, they can achieve a comprehensive end-to-end data management infrastructure.
- Maintenance and Failure Prediction – Edge devices can be programmed to take telematics readings regularly, alerting car owners in case an inspection is required.
They can also be programmed to perform specific functions at the Edge, including monitoring fault information and collecting data from vehicles. The Edge devices collect data from on-site cameras, sensors, and CAN Bus networks of vehicles. Once the information is collated, it can be used to predict failures.
- OEM Manufacturing – Another example of an Edge computing application in a manufacturing environment is the use of sensors to detect failures in production lines. Edge computing solutions can quickly assess the situation and immediately respond to assembly line issues.
Furthermore, OEMs can leverage Edge computing to gather feedback on usage and enhance the next generation of their product lines. Using rugged Edge computers in the production line can allow OEMs to maintain the optimal performance of their equipment.
- Traffic Management - A smart traffic management system can augment vehicle sensor data with external data, such as real-time traffic monitoring or other vehicles' telemetry data. An example of this is truck platooning.
The autonomous platooning of truck convoys has the potential to save fuel costs, reduce congestion, and communicate with ultra-low latency.
- User Experience - Edge computing can be applied in many automotive subsystems, including in-vehicle infotainment systems. These systems have transformed the user experience by providing augmented reality and mobility apps.
The automotive industry needs to retool its business model to make the most of its capabilities. Automakers must invest in Edge computing solutions for their vehicles to make this possible.
Similarly, they must ensure that their Edge-compliant software is secure and reliable. One of the biggest bottlenecks in the data transmission process is vehicle-to-vehicle communication.
However, solutions like high-bandwidth communications and Edge servers can help address this challenge.
The Applications Of Edge Computing In The Motor Insurance Industry

While Edge computing for automotive insurance is still in its infancy, it is being used by several companies to enhance the user experience and improve data processing and safety.
The technology is gaining momentum and is expected to grow. Let us explore these benefits in some detail:
- Efficient Data Processing – Edge computing helps to reduce the time and effort involved in handling vehicle-generated data for processing insurance claims.
Moreover, it also makes it possible to process more data. Therefore, motor insurers can leverage Edge computing to process and handle more claims.
- Improved Safety – Edge computing can improve data handling and users' safety by predicting future scenarios and alerting users about potential problems. Moreover, it can also be used to monitor the health of vehicles.
If a car experiences a fault, it can be detected before a problem becomes threatening. This approach will minimize the risk of car accidents, thereby benefiting the motor insurance industry.
- User Experience – A trustworthy and transparent claims processing solution goes a long way when it comes to customer satisfaction. This technology is often used in conjunction with cloud-based solutions, which can manage large amounts of real-time data.
These solutions can improve user experiences and provide better trust in the system. Furthermore, Edge computing for motor insurance can offer consumers a more personalized experience.
- Automated Vehicle Inspections – Automated vehicle inspections are rapidly becoming a norm in the motor insurance industry. Edge computing enables remote inspections and helps integrate inspection reports with the claims processing flow of insurers. As insurers seek to optimize the claims processing time, AI inspections are the future.
What Is The Relevance Of Edge Computing In Automating Vehicle Inspections?
When insurers and body shops use Edge computing applications for vehicle inspections, they can increase the reliability and quality of their services.
Using an Edge computing platform, they can identify problems before they become problems, saving car owners from the loss of productivity that comes with downtime. Let us explore some advantages of using Edge computing in automating vehicle inspections.
- Decentralized Inspections – Vehicle inspections are performed worldwide in a decentralized manner in contrast to centralized processes such as manufacturing. Edge computing will enable the smooth functioning of this decentralized framework.

- Guided Inspections – The average vehicle owner is not an expert in vehicle inspections and thus requires guidance while conducting a remote vehicle inspection. Customers need real-time feedback on the quality of photos and videos, lighting conditions, and other parameters essential for generating a comprehensive vehicle condition report.
This is challenging to operate through the cloud. For example, let us consider cases where the feedback from the API is delayed. In such scenarios, the customer may have moved away from the car, or the inspection conditions may not be favorable anymore. Edge computing will close these gaps and allow customers to experience a seamless inspection workflow.
- Quick Response Time – Many use cases like car rental require quick assessment of damages and are expected to be processed in 30-60 seconds. Due to latency issues, delivering inspection reports is infeasible if we route them through the cloud. Edge computing enables a quick response time without compromising the reliability or accuracy of the inspections.
Are there Any Downsides?
Having analyzed the benefits, we also have to consider bandwidth issues and the other limitations discussed before. Edge computing has bandwidth issues as some features are unavailable on Edge devices. For example, damage-detection ML models are heavy and require immense processing power, which is not yet available on smartphones.
How Can Inspektlabs Help?
Inspektlabs deploys a hybrid approach. During vehicle inspections, features like car damage detection for select categories happen on the device. For example, glass damage detection occurs through the feedback generated on the Edge device.

In contrast, features like determining the exact OEM part prices, and repair vs. replacement decisions happen on the cloud instead.
As we have discussed, Edge computing has bandwidth issues and other challenges. So, we cannot fully automate all car damages on the Edge just yet. As the technology currently stands, the following processes take place on the Edge:
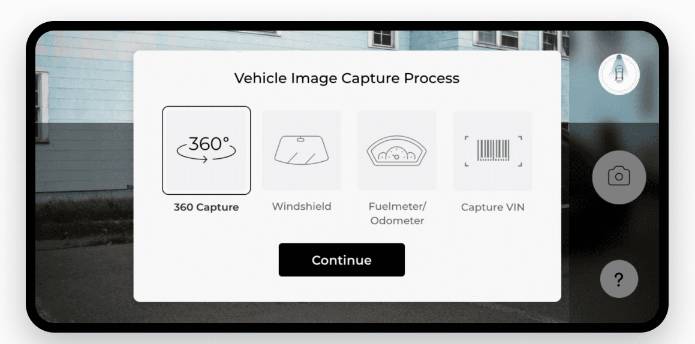
- 360° Guidance – When users engage with Inspektlabs' vehicle inspection software, they have access to 360° guidance that helps them navigate the process of capturing the vehicle. This approach ensures no iteration, and the customer does not need to bother with multiple photos/video submissions.
- Damage Detection for Select Damages – Damage detection for certain damages, like glass damage, occurs on the Edge. Owing to the prevailing limitations, it will take more time to host all damages like dents, scratches, cracks, and others on the Edge.
A hybrid computation with Edge and cloud capabilities enables Inspektlabs to deliver a holistic and reliable framework. Over the long run, Inspektlabs plans to conduct all processes, including car 360° visual assessment, through Edge devices to maximize efficiency.
Conclusion
Edge computing helps improve the efficiency of various applications, including autonomous driving, auto insurance claim processing, and vehicle inspections.
It can help prevent costly downtime and make implementing an enterprise's policies easier. In addition, it can also help boost the performance and reliability of an organization's digital infrastructure.
The use of Edge computing in the automobile sector will invariably increase. Car manufacturers must act quickly to reap the benefits of this new technology.